静态[粘性]渗透率
静态渗透率(或静态粘性渗透率,以避免与静态热渗透率混淆)被定义为空气的动力黏度与静态气流阻抗的比值。通常用符号 k0 表示,其在国际单位制中的维度是 m2(即具有表面维度)。这个参数通常在研究声学和涉及多孔材料的空气流动方面具有重要意义。
Mathematical expression
The mathematical definition of the static permeability, 𝑘0, is:
where the dynamic permeability 𝑘(w) is defined as:
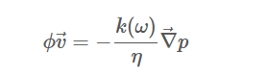
This expression is the generalized Darcy’s law, ϕ is the open porosity. of the material,⃗v the velocity of the fuid particles subjected to the pressure gradient ∇p (ϕ⃗v is thus the fuid fow inside the porous material), η is the dynamic viscosity of air (~ 1.84 x 10-5 N S.m-2 at ambiant temperature and pressure conditions).
The static air-flow resistivity can be deduced from the static permeability:
静态渗透率部分地表征了低频时(当粘性边界层的数量级与孔的特征尺寸相当时)的粘惯性效应。
对于声学材料,静态渗透率的值大致在 [10−11,10−8] m2 范围内。此外,可以证明 𝑘0 应始终小于或等于静态热渗透𝑘0′:
静态渗透率可以从静态气流阻力的测量中推导出来([ISO 9053] 标准致力于对 σ 的测量)。
开放孔隙度:
“开放孔隙度”,通常简称为 “孔隙度”,指的是连续流体相占多孔材料总体积的比例。开放孔隙度通常用希腊字母 ϕ 表示,然而,在 Biot 的原始工作中,h 被用来表示这个参数。
开放孔隙度可以直接测量。[Ber42]

声学多孔介质的示意图。白色区域表示流体相,由连接的孔隙网络组成。封闭孔隙被视为固体相的一部分,用黑色表示。考虑了粘热耗散效应以及死端孔隙的建模工作正在进行中。
对于声学材料,其孔隙度的范围从薄膜或[微]穿孔板(MPP)的小于0.01,到大约[0.70 0.99]。
参考文献:
[Ber42] Beranek L. L., Acoustic impedance of porous materials, J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 13, 1942, pp. 248-260 ■
